All you need to know about special Enzymes
Vulcanchem.com is one of the leading manufacturers and suppliers of high-quality specialty chemicals globally. The substances include building blocks, reagents for new life-sciences, and natural compounds, to name a few. VulcanChem works with academic, industrial, government, developmental, and scientific research firms. The firm has its headquarters in California USA but has several other subsidiaries in Europe, Asia, and North America. VulcanChem hires professionals with excellent academic qualifications and a passion for chemistry and the sciences. One of the leading products by VulcanChem is specialty enzymes. In this article, we discuss specialty inhibitors.
**What
is an Inhibitor?******
An Inhibitor is an agent whose primary role is to interfere with the activity of an enzyme, and inhibitors are also known as enzyme inhibitors. They achieve their purpose by interfering with the binding of enzymes to substrates as well as catalysts. Enzyme inhibitors, therefore, modify the active sites of enzymes and define metabolic pathways.

Types of inhibitors
There are two main types of inhibitors;
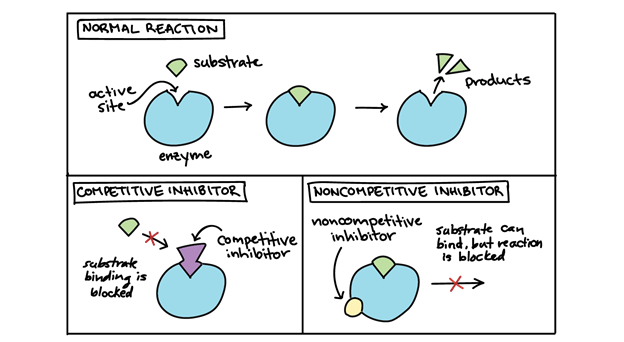
Reversible Inhibitors
Reversible inhibitors are those that are not subjected to chemical reactions when they are linked to the enzymes. This means that they can easily be removed from the compound through dilution or dialysis. Therefore, the effects of reversible inhibitors can be reversed. This type of inhibitors works in such a way that they link to enzymes through non-covalent interactions with the likes of hydrogen and ionic bonds. There are four main types of reversible inhibitors;
- Competitive- competitive inhibitors compete with substrates to bind with the enzymes. The fact that they have a similar structure as the real substrate works to their advantage- Non-competitive inhibitors- the binding of this type of inhibitor does not affect the binding of the substrate- Uncompetitive inhibitors- these are inhibitors that only link to the substrate-enzyme complex. - Mixed inhibitors- these are inhibitors that bind to enzymes as well as substrates at the same time.

Irreversible inhibitors
Irreversible enzymes are those whose reaction cannot be reversed. This means that they completely modify the enzymes as they are bound to it using covalent bonds. This type of inhibitors is specific to a unique class of enzymes and not all types of proteins. They also do not function by destroying the structure of the enzyme but merely altering the active site of the enzyme. Irreversible inhibitors can also bind with enzymes in more than one way. For instance, a single compound can be bound both irreversibly and reversibly.
**Applications
of Inhibitors******
- Healthcare- inhibitors are used as drugs to treat diseases. They are intended in such a way that they target a unique human enzyme to correct a specific pathological condition. For instance, some enzymes treat diseases by causing less or more production of a catalyst. Inhibitors are also used in the manufacture of antibiotics- Metabolic control- inhibitors are vital in metabolic control. - Pesticides- pesticides are made mostly from enzyme inhibitors that alter the production of specific enzymes in animals.
Bottom Line
Inhibitors can either be produced naturally or artificially. Artificial enzymes are mainly used in the manufacture of drugs. On the other hand, natural inhibitors can be applied as natural poisons.

